Receivables financing is when a business transforms its outstanding accounts receivables (AR) into cash via a financing facility using the receivables as collateral. These receivables are invoices issued to customers, but the payment has not been made yet.
Receivables financing is a form of invoice financing.
![]() Highlights of this article:
Highlights of this article:
- Accounts Receivable vs Accounts Payable
Same thing, different point of view; an invoice is an asset for one company but a liability for the other - Which Industries or Business Types are Ideal for Receivables Financing?
Learn the receivables financing advantages and disadvantages
Content
Companies often view receivables as a burden because substantial wealth is trapped and cannot be converted into cash until the payment is due.

To understand how to convert the asset into cash, we first need to introduce the concept of Accounts Receivables (AR) and Accounts Payable (AP).
Differences Between Receivables and Payables
From an accounting perspective, accounts receivable (AR) is money owed to a company by its customers, whereas accounts payable (AP) is money the company owes to its suppliers.
While receivables are current assets on a company’s balance sheet, payables are current liabilities. Both the assets and liabilities are short-term in nature.
Accounts receivable and accounts payable are different faces of the same coin; the same invoice is an asset for one company and a liability for the other.
Let’s take a look at an example.
Receivables vs Payables Example
A paper manufacturer issues an invoice to a printing company related to purchasing paper stacks to produce books.
On the balance sheet of the printing company, this specific invoice is an account payable.
The company sells the books on the Amazon eCommerce platform. In this case, the invoice issued to Amazon is an account receivable on the printing company’s balance sheet.
For this reason, receivables financing is also a type of asset-based lending.
Brought to you by Velotrade, a marketplace for corporates to access financing.
Like our content? Follow us!
Is Receivables Financing Suitable for Your Business?
Receivables financing, like other invoice financing facilities, has its benefits and drawbacks depending on the nature of the business and its needs.
Let’s have a look at it.
IDEAL SCENARIOS
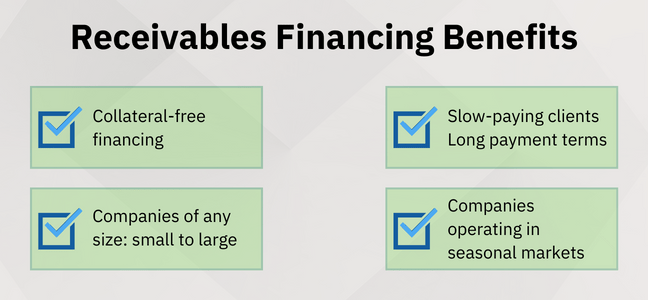
Receivables financing is ideal for businesses with regular sales on credit as they tend to suffer from structural cash flow gaps.
The reason is simple: these companies must pay the inventory before receiving any payment for goods sold.
A substantial problem could arise if multiple clients simultaneously ask to extend payment terms. In this case, the cash flow gap would widen even more!
To avoid this issue, the accounts receivables financing facility helps cover cash shortfall by advancing money for the outstanding invoices. By doing so, the business can:
- Speed up the business’ cash cycle
- Reduce the Days Sales Outstanding (basically the number of days it takes to collect payment)
Accounts receivable financing is also ideal for businesses operating in seasonal markets. These companies experience a sudden increase in cash outflow during peak production as their payment collection is deferred.
Consequently, it gets difficult for the company to fulfil larger customer orders.
Receivables financing can help meet a business’s immediate cash flow needs during such periods.
Providing and risking collaterals is eliminated; the invoice serves as collateral for the funding.
For this reason, receivables financing is also popularly known as invoice discounting.
Want to know more about Invoice Discounting?
Unwind the 2 key benefits of Invoice Discounting and get familiar with this financing facility.
LESS IDEAL SCENARIOS
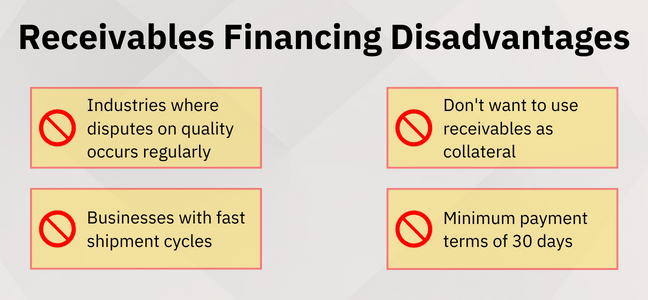
However, there are instances when receivables financing may not be a suitable solution for a business.
Since receivables financing requires a business to use its receivables as collateral, firms with a greater chance of bad debt would not want to risk opting for this approach.
Businesses operating in sectors or industries where disputes on quality and damage are commonplace would also not be suitable. In this case, buyers can use defects and poor product quality as an excuse not to pay.
The facility requires a minimum payment term of 30 days. Businesses with faster shipment cycles and shorter payment terms of 14 or 7 days, such as retailers or eCommerce shops that incorporate just-in-time delivery, would not be ideal.
In such cases, businesses can understand the invoice factoring process and have their debt collection process outsourced.
Receivables Financing Example
A business sells kitchen equipment to restaurants and hotels. They receive a large purchase order from a national restaurant chain (the debtor).
The debtor is willing to buy the equipment worth $400,000.
The restaurant needs the equipment but can only make the payment 2 months later.
The business accepts the terms, produces and delivers the equipment and issues an invoice of $400,000 due 60 days later.
When applying for financing, the financier considers two critical variables for the application:
- The creditworthiness of the buyer (the debtor)
- The quality and length of the buyer-seller commercial relationship
Upon approval, the financier advances $316,000 to the kitchen equipment manufacturer.
Get a detailed breakdown of the cost of invoice financing to understand how the advanced amount is calculated.
Once the debtor pays the full amount by the due date, the financing company will release the remaining $84,000 minus a discounting fee.
By doing so:
- The manufacturer gets access to cash immediately
- The client gets the equipment it needs and gets to pay later
- The financier profits from the financing fees
It is a win-win-win situation for all involved parties.
Since receivables financing is a type of invoice-based lending, the financing process is essentially the same.
Unlock how invoice financing works to know the process flow.