Overseas trading is usually a long and complicated process due to all the logistics involved. Importers and exporters face several costs and risks: from tariffs and taxes to currency fluctuations, non-payment, and non-shipment risks.
Import and export finance are a type of supply chain finance that help facilitate trade.
![]() Highlights of this article:
Highlights of this article:
- The Export-Import Trading Cycle
How every business is both an exporter and importer - Benefits for Exporters and Importers
Discover the reasons why businesses enrol into export-import finance - Example: Optical Devices Provider
We illustrate how a Singapore-based manufacturer completes the trading cycle successfully
Content
What is Export Finance?

Export finance is a cash flow solution for exporters selling goods overseas.
Since the buyer often pays within an agreed payment term (most commonly between 30 to 120 days), the seller faces a cash flow issue.
Export finance allows businesses to access working capital before clients pay for goods purchased.
What is Import Finance?

Import finance is the other half of the supply chain that provides funding to the buyer to purchase goods exported from overseas.
Importers purchasing goods also need to cover their expenses while waiting for the products to arrive.
Import finance helps bridge this gap between the purchase and delivery time of goods.
This can be achieved in 2 ways:
- Purchase Order Finance
Businesses use this facility to finance the purchase of goods requested in the purchase order.
In this case, the importer can solely use the funds to pay for production expenses incurred for goods stated in the PO.
- Loan
When an importer needs capital to procure materials for goods not backed by a PO, it is classified as an import loan.
The good being imported acts as the collateral in this case.
An importer may need these materials to increase inventory safety margin, meet peak season demands, or shorten the trade cycle.
Brought to you by Velotrade, a marketplace for corporates to access financing.
How Does Export and Import Finance Work?
It is often common for buyers to request 30-120 days payment terms to pay for goods. This sales-to-revenue gap means that even though the exporter has already shipped the products, he will receive the payment once the invoice is due.
To overcome this cash flow issue, the exporter applies for export financing.
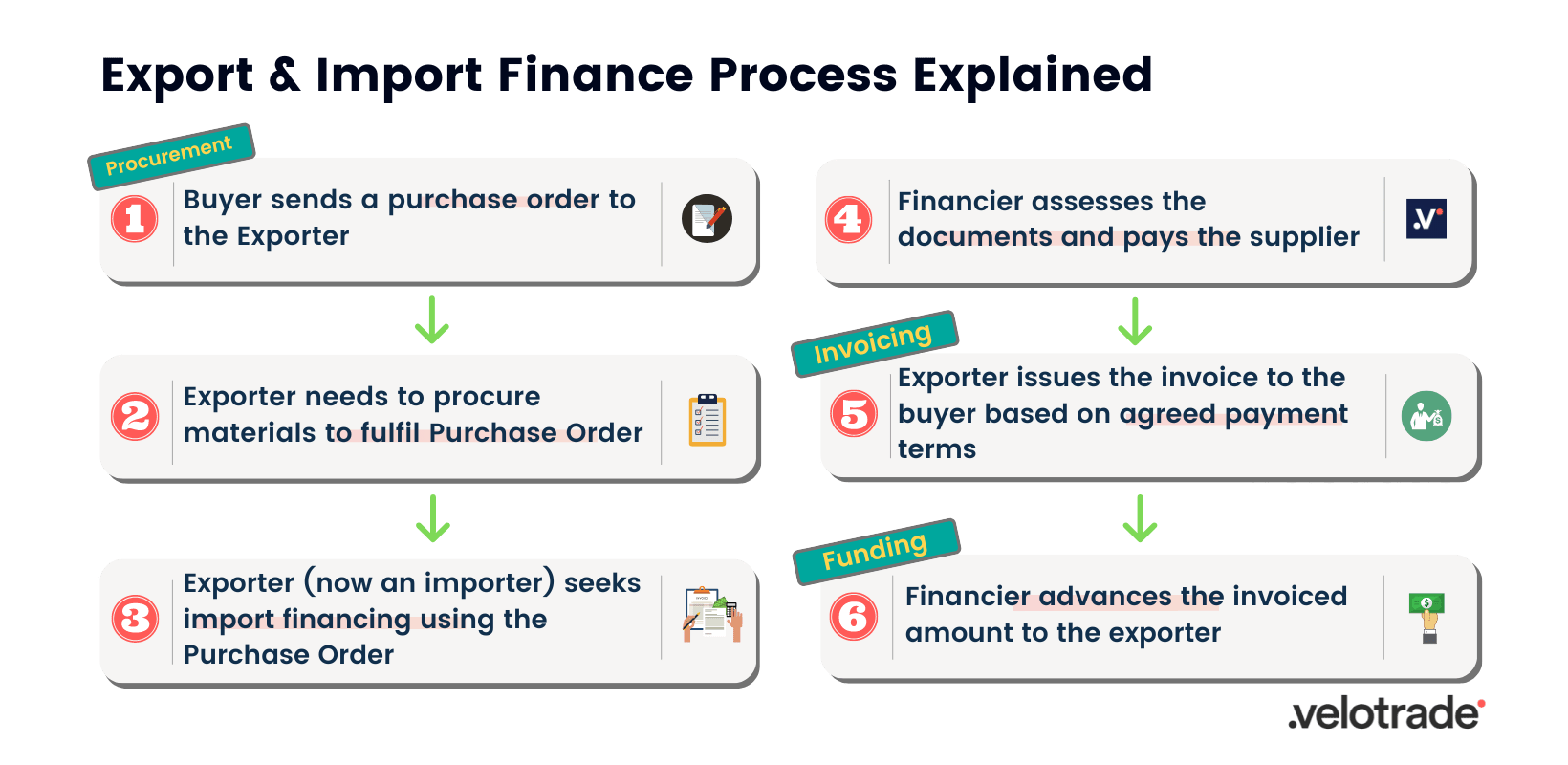
Since export finance is attained after an invoice is issued, the process is the same as post-shipment supply chain finance.
It is important to note that supply chain players could be both importers (buyer) and exporters (seller) at the same time.
The financier assesses the buyer’s creditworthiness, the importer-exporter relationship and their financial track record before releasing funds.
Once the importer passes credit assessment, the financier funds a percentage of the cost of goods to the supplier for supplies procured by the importer.
This importer then becomes an exporter to its buyer, who has requested a purchase order with deferred payment terms.
The seller then seeks export financing to bridge the payment gap and complete the trade cycle.
Find out how Velotrade bridges the bank funding gap with a real business example!
Importance of Export and Import Finance
A significant benefit for exporters and importers is to reinvest the funds in business operations and growth while maintaining their regular cash flow cycle.
Export and import finance help reduce the trading gap caused due to payment terms and extended shipping time. The facilities also help mitigate shipping and financial risks.
As every importer is also an exporter and vice versa, the capacity to sell and buy goods expands along with their ability to offer credit terms.
Benefits For Exporters
Security of payment is probably the most important benefit for exporters. Once the counterpart is enrolled to financing they will certainly receive cash advance from the financier. However, in case of buyer default of payment, the exporter could be responsible to repay the debt at maturity.
Also, fees are pre-agreed, protecting both parties from any interest or currency fluctuations during the settlement period.
Some lenders also use Export Credit Agencies that provide insurance and loan guarantees on goods sold overseas, limiting some of the risk exposure. However, in recent years trade credit insurance are reducing their exposure significantly.
Find out the different financial intermediaries that borrowers can access to facilitate their trade finance transactions.
Benefits For Importers
Likewise, importers attain the financial capability to undertake more orders and pay advance to their suppliers. This speeds up the trade cycle.
All this is achieved without any equity, angel, or private investment.
Overall, the facilities foster trade for exporters and importers in the trade finance ecosystem. A greater sense of confidence and security is instilled among manufacturers, buyers, and sellers, creating a win-win-win situation for all parties.
![]() Key Takeaways
Key Takeaways
- An Exporter Could be an Importer (and vice versa) in the Supply Chain
As importers transform raw materials, they become exporters if the final product is sold abroad. - Improving Productivity of Global Trade
While export finance helps exporters bridge payment gaps for buyers, import finance gives the borrower capital to procure materials and complete the order.
Export and Import Finance Business Example
So, now that you understand the process and its importance, let’s walk through an example.
Imagine a laptop manufacturer based in Singapore that sources from China and have buyers based in USA and UAE.
Their American buyers who work on 90-120 days payment terms have requested a large purchase order of 500 laptops.
To fulfil this order, the company must make upfront payments to its Chinese optical distributor for materials. Meanwhile, it needs capital to fulfil other orders.
It cannot afford to wait 90-120 days to receive payment.
The company seeks a financier to meet and expand its exporting and importing capacity. With import finance, the manufacturer can pay the supplier cash advance and procure the cables needed to produce and fulfil the order.
Before doing so, the manufacturer must beware of purchase order financing costs.
The manufacturer then issues the invoice to the buyer and secures 70-80% of the payment (minus fees) with export financing. This cash advance can be used to procure the next batch of raw materials.
Export finance fees are equivalent to post-shipment supply chain finance costs as it is an invoice-based solution.
This example shows how export and import financing helps the manufacturer complete and optimise the trading cycle.
Customised
Diverse
Global
Velotrade's dynamic Supply Chain Finance solution fulfills corporate's large trade volumes financing imports and exports from multiple suppliers.