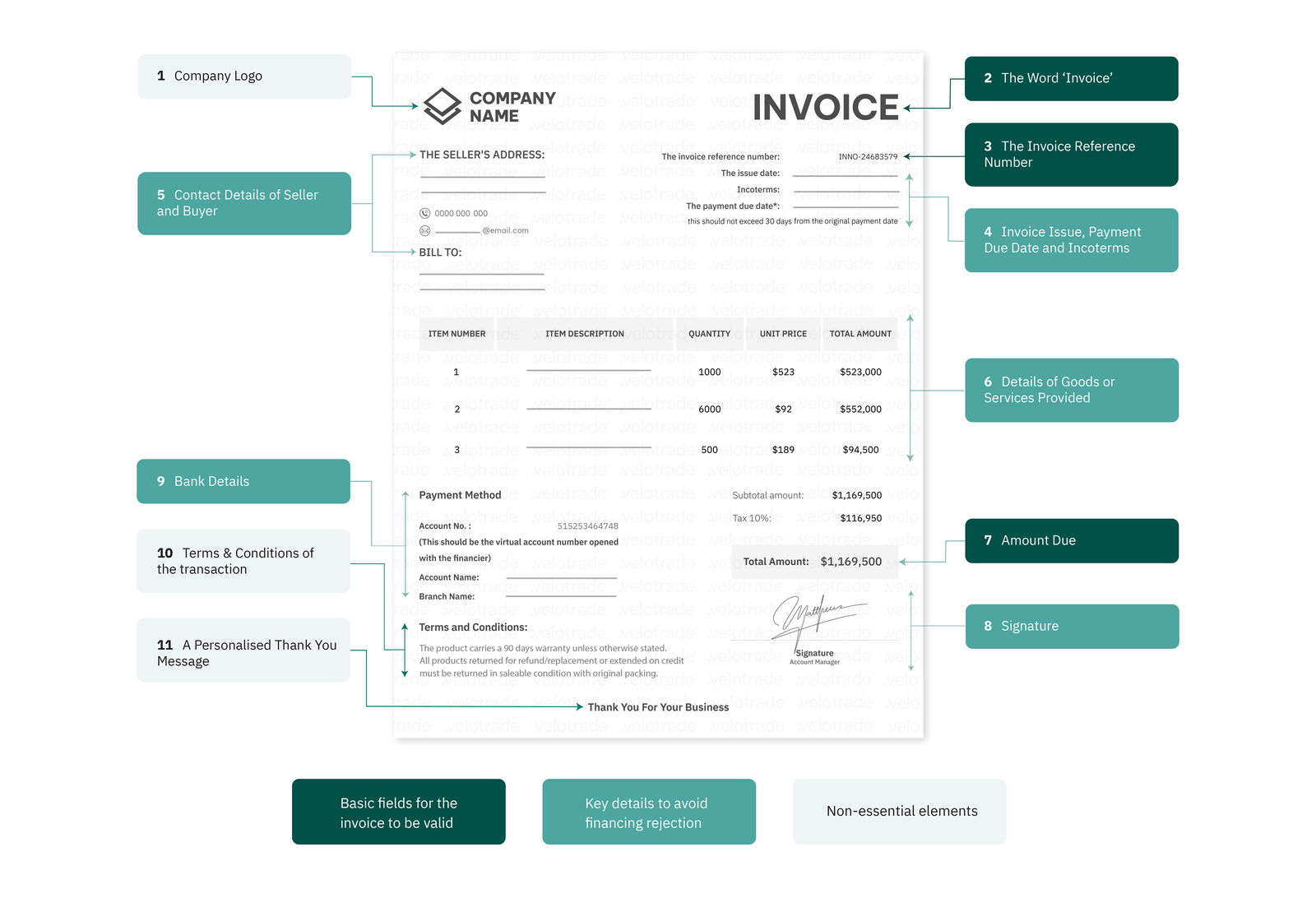
Supply chain finance (SCF) is essential to supply chain management. It connects buyers & suppliers with a financing institution to lower financing costs, improve cash flow efficiency, and reduce risks.
Highlights of this article
- Importance of Supply Chain Finance Simply put, it’s flexible, efficient, and beneficial to Supply Chain Management. How so?
- How does SCF work? Illustrate the process flow of SCF with a financing company
- Examples and Calculation A clear breakdown of the costs and fees with an easy-to-understand scenario
- How to Apply Who can apply? How to apply?
SCF in Global Markets
Supply Chain Finance protects business transactions and promotes import & export activities globally. It consists of a range of products to fit medium-sized and big corporates.
PO financing and the broader suite of invoice financing solutions are the most common products.
The parties involved in SCF are the typical trade finance players: the buyer connects its suppliers to the financial institution.

Supply chain finance represents a win-win-win situation (3 parties, 3 winners) for the reasons assessed below.
Why is Supply Chain Finance Important?
SCF is important in promoting global import & export activities as it adds flexibility and protection to commercial transactions.
How? Let’s dig a bit deeper.
International trade takes a longer shipping time compared to domestic transactions.
Current market practices allow buyers to negotiate and extend payment terms. For example, it can take 30 to 120 days from the delivery of goods to the settlement of the invoice.
Velotrade platform data shows that 57 days is the average agreed payment term.
Suppliers could apply for financing and receive cash immediately to fill this payment gap.
An Efficient Financing Model
Supply Chain Finance relies on the buyer-supplier relationship and the buyer’s involvement in the financing application.
A strong buyer’s creditworthiness adds weight to evaluating suppliers’ credit limits. Suppliers can access financing at a lower price with the buyer’s involvement.
Verifying the buyer-supplier relationship is essential to credit assessment.
SCF Enhances Supply Chain Management
A financing programme helps with supply chain management and improves the suppliers’ productivity. It allows suppliers to increase stocks, pay salaries, and even invest in infrastructure.
The importance of buyers in strengthening the business relationship with suppliers also helps suppliers’ financial health.
Thus, supply chain finance benefits exporters and importers in the trade ecosystem.
Supply Chain Financing improves trade conditions for both sides:
- Buyers can negotiate payment terms with suppliers and reduce the risk of supplier default.
- Likewise, suppliers can better manage their cash flows with access to cheaper financing.
The Role of the Financing Institution
First and foremost, the financial institution is responsible for running due diligence and Know-Your-Client procedures on its counterparts.
These procedures help minimise the risks involved in the financing process.
As part of the SCF risk management, the financial institution carefully analyses the creditworthiness and the length of the commercial relationship.
Upon confirming the contracts, the institution transfers the advanced amount to the suppliers.
The company charges a commission based on the notional amount, the financed days, and the agreed-upon rates.
The institution will charge a fee based on the transaction amount to oversee the financing process.
Brought to you by Velotrade, a marketplace for corporates to access financing.
Get practical insights with the 2 supply chain finance business scenarios!
How Does Supply Chain Finance Work?
The shipment of goods marks an essential sequence for SCF; it dictates the facilities most suitable for financing.
Before shipments, purchase order financing is the go-to solution for businesses seeking to join SCF programme.
After shipments, supply chain financing is usually fulfilled through invoice financing solutions.
Process Flow
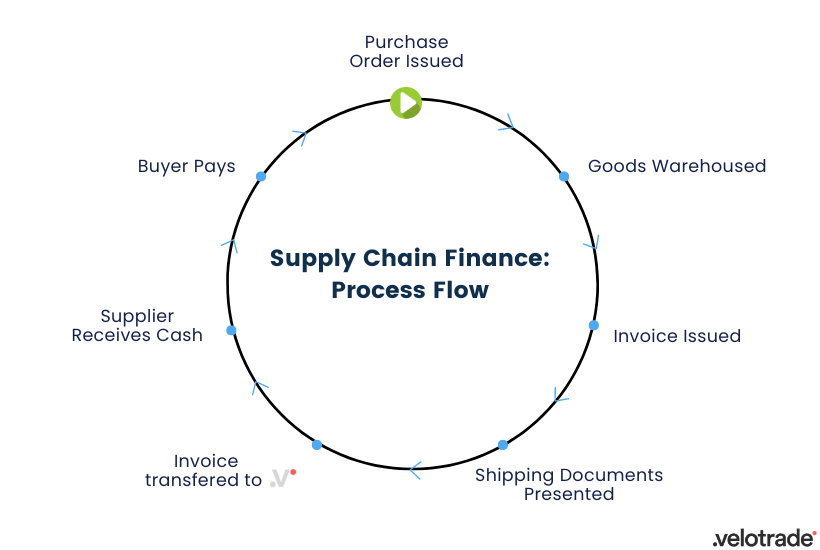
The process is summed up in the following steps:
- KYC and due diligence are performed on the buyer and its suppliers. These procedures validate that both sides are eligible for SCF services.
- The Supplier invoices the buyer and then transfers the invoice to the financing company.
- The Financing Company advances about 80% of the notional amount.
- At maturity, the Buyer pays the whole amount of the invoice. Then the funds are transferred to the financing company accounts.
- The Financing Company re-pays the supplier the remaining 20% minus the agreed fees.
![]() Key Takeaways
Key Takeaways
- Supply Chain Finance is Crucial to International Trade It protects the supply chain by injecting liquidity and closing the cash flow gap.
- Efficient Global Trade Financing enhances the business capacity of suppliers and thus the overall supply chain productivity.
- **Better Deal Conditions **With financing in place, buyers and suppliers can negotiate better terms under strengthened financial health and reduced default risks.
Costs and Fees: An Example
ABC limited (the buyer) is a retail company based in Hong Kong. The supplier is Shoes Pte, with a specialisation in manufacturing white socks.
They both agree on the following terms specified on the purchase order:
- Shoes Pte agrees to produce 1,500,000 pairs of white socks at $0.85 a pair. The total amount is $1,275,000.
- Payment terms are 60 days after the issuance of the invoice. The invoice contains the goods description, the quantity and delivery terms.
At this stage, Shoes Pte has two options to consider:
Q
Do nothing and wait for 60 days before the invoice is settled
R
Apply for supply chain finance with a reputable institution
However, Shoes Pte does not want to wait 60 days to receive payment from ABC limited, while ABC limited needs cash to pay other expenses and wants to hold on to optimise its working capital.
How can ABC limited extend payment terms with Shoes Pte while fulfilling their immediate payment requests?
It can apply for a Supply Chain Finance Programme with a reputable financial institution like Velotrade.
Breakdown of the Costs and Fees
The supplier and the financial institution negotiate the terms of the financing.
The following terms were agreed upon:
%
Total
Financing Days
-
60
Invoice Amount
100%
1,275,000.00
Financing Amount
80%
1,020,000.00
Servicing Fees
1%
12,750.00
Interest
8%
13,413.70
Repayment at Maturity
20% - interest
241,586.30
Shoes Pte sells the invoice to the financing company, and it receives an immediate transfer of $1,020,000 – $12,750 = $1,007,250 directly in the bank account.
Wondering how the calculation works?
Since this is post-shipment supply chain finance, meaning that the invoice is already issued, cost calculations are equivalent to the costs of financing an invoice.
Fast-forwarding 60 days…
Firstly, ABC Limited (the buyer) pays back the financing company the full invoice amount of $1,275,000.
Then, the financing company transfers the remaining 20% of the invoice minus interest to Shoes Pte.
That is, $255,000 – $13,413.7 = $241,586.3 is the amount transferred into Shoes Pte’s bank account.
Supply chain financing allows ABC limited to pay 60 days later while providing cash advance to Shoes Pte to meet their immediate cash flow needs. This optimises the cash flow of both parties.
Likewise, ABC limited can finance multiple such suppliers through supply chain finance.
The buyer can raise a commercial dispute if the supplier provides non-compliant, defective, or damaged goods.
The financing company may request the supplier to pay back the advanced amount.
Fees and any interest accrued will also be charged to the supplier.
Bridging Banks’ Supply Chain Finance Gap
Supply chain finance programs are designed to bridge the payment gap. However, banks’ lengthy and tiresome document approval process can take nearly a month to transfer funds.
At this stage is where alternative financiers like Velotrade can help.
How?
Let’s look at a real case to find out!
Imagine the below case scenario:
- Supplier – Furniture manufacturer
- Annual Turnover – 88M
- Buyers – Big supermarkets and retailers in the US
- Payment Terms – 220 days
The supplier receives purchase orders as large as $50M per year and needs instant liquidity to pay manufacturers.
The supplier connects to a bank hired by its buyer to seek supply chain financing. However, the bank takes about 21 days to verify all documents. The supplier cannot afford to wait for 21 days, especially during peak seasons like July and August.
Hence, it seeks help from an alternative financier.
Velotrade’s digital process further reduces this gap!
The supplier uploads documents on the Velotrade platform and the bank portal simultaneously.
Velotrade spot-checks all documents and releases funds in just 3 days! Meanwhile, the bank verifies and repays the financed amount on the 21st day.
This creates value for both buyers and suppliers.
How to Apply For Supply Chain Finance?
Both the buyer (on behalf of its suppliers) and the supplier can apply for Supply Chain Finance.
Suppliers must be in business for over 2 years generating a turnover of over USD 1 million.
Understand how our supply chain solution works, and reach out to us!
Optimise your Supply Chain
Flexible Customised Diverse Global
Velotrade's dynamic Supply Chain Finance solution fulfills corporate's large trade volumes financing imports and exports from multiple suppliers. See supply chain financing options